Average Cost for Windows and Siding A Comprehensive Guide
The average cost for windows and siding is a crucial factor when planning a home renovation. Understanding the price variations involved is key to budgeting effectively. This guide will break down the costs associated with different materials, installation methods, and regional factors, empowering you to make informed decisions for your project.
From the type of window (double-hung, casement, or bay) to the siding material (vinyl, wood, or fiber cement), numerous choices impact the final cost. We’ll explore the price differences between energy-efficient and standard options, the influence of project size, and how labor costs compare to material costs. Additionally, we’ll examine regional variations in pricing and highlight potential unexpected expenses, helping you create a realistic budget.
Defining “Average Cost”: Average Cost For Windows And Siding

Source: remodelingimage.com
Understanding the average cost of window and siding replacement is crucial for budgeting your home improvement project. However, “average cost” is a relative term, heavily influenced by several factors. This section will clarify the variables that contribute to the final price, helping you develop a more realistic budget.
Material Type and Cost Variation
The materials used for windows and siding significantly impact the overall cost. Vinyl is generally the most affordable option, offering a balance of durability and cost-effectiveness. Fiberglass windows and siding are more expensive but boast superior energy efficiency and longevity. Wood provides a classic aesthetic but requires more maintenance and is typically the priciest choice. Aluminum siding is a budget-friendly option but may not offer the same insulation value as other materials. These differences in material properties directly translate into variations in price per square foot.
Installation Method’s Influence on Cost
The installation process itself contributes substantially to the final cost. A complex installation, such as replacing uniquely shaped or unusually sized windows, or working on a multi-story home with difficult access, will increase labor costs. The level of experience and expertise of the installation crew also affects the price. Experienced installers may charge more per hour but their efficiency can sometimes offset the higher hourly rate, leading to a faster project completion. Simple, straightforward installations on single-story homes with standard window and siding sizes will generally be less expensive.
Labor versus Material Costs
A typical window and siding replacement project typically sees a split between material and labor costs. While the exact ratio varies depending on the project’s complexity and the chosen materials, labor often accounts for 30% to 50% of the total cost. High-end materials will naturally increase the material cost percentage, while complex installations will inflate the labor cost component. Accurate budgeting requires obtaining separate quotes for materials and labor to understand the cost breakdown clearly.
Average Cost Comparison Table
| Material | Average Cost/sq ft (Low) | Average Cost/sq ft (High) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding | $3-$5 | $8-$12 | Widely available, relatively inexpensive, and requires less maintenance. |
| Fiber Cement Siding | $8-$12 | $15-$25 | Durable, fire-resistant, requires less maintenance than wood. |
| Wood Siding | $10-$15 | $25+ | Aesthetically pleasing, requires regular maintenance and painting. |
| Aluminum Siding | $2-$4 | $7-$10 | Budget-friendly, and low maintenance, but may dent easily. |
| Vinyl Windows | $100-$200 | $300-$500 | Cost-effective, low maintenance. |
| Fiberglass Windows | $200-$400 | $600-$1000+ | Energy-efficient, durable, long lifespan. |
| Wood Windows | $300-$600 | $1000+ | Aesthetically appealing, requires regular maintenance. |
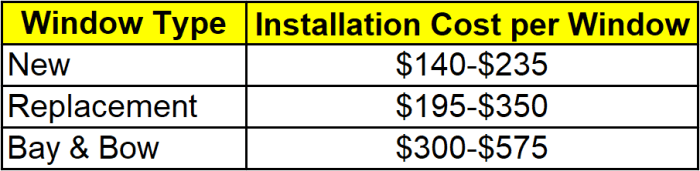
Window Types and Costs

Source: scottishhomeimprovements.com
Choosing the right windows significantly impacts both the aesthetics and energy efficiency of your home. Different window styles offer various benefits and come with a range of price points. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions during your home improvement project. This section will break down the costs associated with various window types, considering factors like energy efficiency and size.
Window Style Costs and Energy Efficiency
The cost of windows varies considerably depending on the style, material, size, and energy efficiency features. Generally, simpler styles tend to be less expensive, while more complex designs, such as bay or bow windows, command higher prices. Energy-efficient windows, incorporating features like multiple panes of glass and low-E coatings, also increase the initial cost but offer significant long-term savings on energy bills.
Window Type Cost Comparison
The following table illustrates the approximate cost variations among different window types. Remember that these are average costs and can fluctuate based on factors such as the manufacturer, materials used, and regional pricing. Energy efficiency ratings are represented by U-factors (lower is better) and Solar Heat Gain Coefficients (SHGC) (lower is better for reducing heat gain). These values are illustrative and specific ratings will vary depending on the window’s construction.
| Window Type | Average Cost (per window) | Energy Efficiency Rating (U-factor/SHGC) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double-Hung | $200 – $800 | 0.25-0.35 / 0.25-0.35 | Standard and energy-efficient options are available. Cost varies greatly depending on size and features. |
| Casement | $250 – $900 | 0.20-0.30 / 0.20-0.30 | Often more energy-efficient than double-hung due to tighter seals. |
| Bay/Bow | $1000 – $3000+ (per unit) | 0.25-0.40 / 0.25-0.40 (varies widely based on the number and type of windows) | More expensive due to their complex design and increased materials. |
| Sliding | $150 – $700 | 0.25-0.35 / 0.25-0.35 | Similar in cost to double-hung windows. |
| Fixed/Picture | $100 – $500 | 0.20-0.30 / 0.20-0.30 | The least expensive option, as they are non-operable. |
Impact of Window Size and Quantity
The overall project cost is directly proportional to the number and size of windows being replaced or installed. Larger windows naturally require more materials and labor, leading to higher individual costs. A project involving ten large bay windows will be significantly more expensive than a project replacing five smaller double-hung windows. For example, replacing five standard-sized double-hung windows might cost between $1000 and $4000, while replacing five large bay windows could easily cost $5000 to $15000 or more. Accurate cost estimation requires detailed measurements and a comprehensive quote from a window installation professional.
Siding Materials and Pricing
Choosing the right siding for your home involves considering not only aesthetics but also long-term costs. Different materials offer varying levels of durability, maintenance requirements, and initial investment, impacting your overall budget significantly. This section provides a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision.
Several factors influence the final cost of siding installation beyond the material itself. These include the size and complexity of your home’s exterior, the need for repairs or underlying structural work, labor costs in your region, and the chosen installer’s experience and overhead. A simple, single-story home will naturally cost less to side than a multi-story house with intricate architectural details.
Siding Material Cost Comparison
The following table offers a comparative analysis of common siding materials, focusing on average costs per square foot (sq ft) installed. Remember that these are estimates and can vary depending on location, material quality, and labor costs.
| Siding Material | Cost per sq ft (Installed) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $3-$12 | The lower end represents basic styles; the higher end includes premium colors and textures. |
| Wood | $10-$30+ | Cost varies greatly depending on wood type (e.g., cedar, redwood) and quality. Requires significant maintenance. |
| Fiber Cement | $8-$20+ | Offers excellent durability but a higher initial cost compared to vinyl. |
| Metal (Aluminum or Steel) | $7-$25+ | The cost depends on the type of metal and finish. Very durable and low-maintenance. |
Factors Influencing Siding Installation Costs
Several factors beyond material selection impact the overall cost of siding installation. Understanding these will help you budget effectively. For instance, a larger home with multiple gables and dormers will require more time and materials, leading to a higher installation cost than a smaller, simpler structure. The presence of existing damage requiring repair before installation also adds to the expense. Finally, regional labor rates and the installer’s experience and reputation will influence the final price. A highly skilled and experienced installer might charge more per hour but potentially deliver a superior and more durable installation.
Siding Material Longevity and Maintenance
The long-term cost of siding is significantly influenced by its lifespan and maintenance needs. A material with a longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements ultimately proves more cost-effective in the long run, despite potentially higher upfront costs.
- Vinyl: Generally lasts 20-30 years with minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning is sufficient.
- Wood: Requires regular painting or staining (every 3-5 years) and can be susceptible to rot, insect damage, and warping, leading to frequent repairs and potentially shorter lifespan if not properly maintained. A well-maintained wood siding can last 50 years or more.
- Fiber Cement: Highly durable and can last 50 years or more with minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning and repainting every 15-20 years are typical.
- Metal: Extremely durable and low-maintenance; can last 50 years or more with minimal upkeep; occasional cleaning is usually sufficient.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Siding Material
This section summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each siding material, including cost implications.
- Vinyl Siding:
- Advantages: Affordable, low maintenance, variety of colors and styles, easy installation.
- Disadvantages: Can be easily damaged, may fade over time, not as durable as other options.
- Wood Siding:
- Advantages: Classic look, and natural beauty, can increase home value.
- Disadvantages: High cost, high maintenance (painting, staining), susceptible to damage from weather and insects.
- Fiber Cement Siding:
- Advantages: Durable, fire-resistant, low maintenance, long lifespan.
- Disadvantages: Higher initial cost than vinyl, can be brittle and prone to cracking if improperly installed.
- Metal Siding:
- Advantages: Very durable, low maintenance, long lifespan, fire-resistant.
- Disadvantages: Can dent, higher initial cost than vinyl, and may be noisy during rain.
Regional Cost Variations
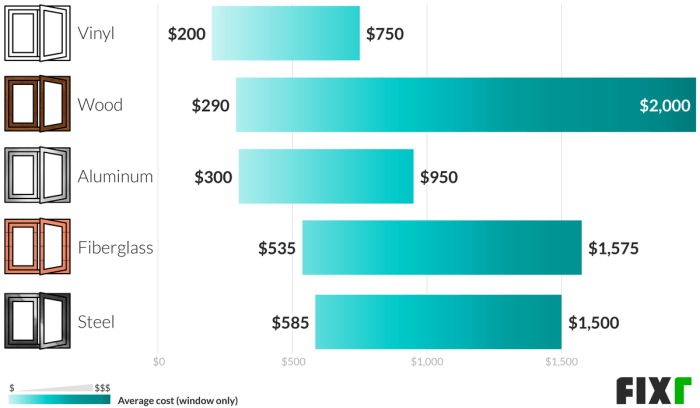
Source: fixr.com
The cost of window and siding installation varies significantly across the United States, influenced by a complex interplay of factors related to geography. These variations are not simply about differences in the price of materials; they also reflect regional disparities in labor costs, material availability, and local regulations. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for accurate budgeting and realistic project planning.
Regional differences in labor rates are a major factor. Areas with high costs of living, such as major metropolitan areas on the coasts, tend to have higher labor rates for contractors. Conversely, more rural areas or regions with lower overall costs of living often have lower labor rates. This directly impacts the overall installation cost, as labor represents a significant portion of the total expense. For example, a window installation project in New York City might cost considerably more than a similar project in rural Nebraska, even if the materials are identical.
Labor Rates and Material Availability
Labor costs vary widely across the country. Highly populated coastal regions like California, New York, and Florida typically command higher wages for skilled tradespeople, leading to increased labor costs in window and siding projects. Conversely, less populated areas in the Midwest and South often have lower labor rates. Material availability also plays a role. Transportation costs and regional demand influence the price of materials. For instance, certain types of wood siding might be more readily available and therefore less expensive in regions with abundant timber resources, while other materials might be more expensive in areas far from manufacturing hubs or major distribution centers. This can create substantial differences in material costs between regions.
Influence of Local Building Codes and Regulations
Local building codes and regulations significantly influence project costs. Stricter codes, often found in areas prone to severe weather events (hurricanes, earthquakes, etc.), may necessitate the use of more expensive, higher-performance materials. Permitting processes can also vary widely, with some areas having more streamlined and less expensive processes than others. For example, coastal regions with stringent hurricane-resistant building codes might require impact-resistant windows and reinforced siding, adding substantially to the overall project cost compared to areas with less demanding codes. Similarly, areas with complex permitting processes might add administrative costs and delays to the project.
Regional Cost Map
Imagine a map of the contiguous United States. The coastal regions – particularly the West Coast (California, Oregon, Washington), the Northeast (New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts), and parts of the Southeast (Florida, parts of Georgia, and the Carolinas) – are depicted in a darker shade of red, indicating higher costs for window and siding installation. A lighter shade of red represents areas with moderately higher costs, such as parts of Texas, Illinois, and Colorado. The central and some southern regions (large parts of the Midwest and South) are shown in a lighter shade of green, representing areas with lower installation costs. Finally, the darkest green represents the lowest cost regions, primarily in sparsely populated areas of the Midwest and the Plains states.
Cost Range Key:
Darkest Red: Highest Costs (>$25/sq ft for siding, >$1000/window)
Light Red: Moderately High Costs ($15-25/sq ft for siding, $600-1000/window)
Light Green: Moderately Low Costs ($10-15/sq ft for siding, $400-600/window)
Darkest Green: Lowest Costs (<$10/sq ft for siding, <$400/window)
Note: These are broad generalizations and actual costs can vary within each region depending on specific factors.
Additional Project Costs
Replacing windows and siding is a significant home improvement project, and while the cost of materials and labor forms a large part of the overall expense, several additional costs often arise. Understanding these potential expenses beforehand is crucial for accurate budgeting and avoiding unpleasant surprises during the project. Failing to account for these extras can lead to project delays or even necessitate cutting corners on quality.
It’s important to remember that the total cost of your project will extend beyond the initial estimates for windows and siding. Several factors can influence the final price, some predictable and others less so. Careful planning and budgeting are key to managing these costs effectively.
Permitting and Inspections
Obtaining necessary permits from your local municipality is a common additional expense. Permit fees vary significantly depending on your location, the scope of the project (number of windows and siding area), and the complexity of the work. For example, a large-scale siding replacement might require a more extensive permit and associated fees compared to a smaller window replacement project. Furthermore, inspections are typically required at various stages of the project, adding to the overall cost. These inspections ensure the work meets local building codes and safety standards. Expect to allocate a budget specifically for these official processes.
Demolition and Waste Removal
Before installation can begin, the existing windows and siding must be removed. This demolition process involves labor costs and potentially specialized equipment rental, especially for difficult-to-remove materials or older construction. The disposal of the old materials also incurs costs, including transportation to a landfill or recycling facility. The amount of waste generated will influence the final disposal fee; larger projects naturally produce more waste. For example, a house with extensive brick moldings around its windows might require more demolition time and therefore higher labor costs.
Unforeseen Repairs and Issues
During the removal and installation process, unforeseen issues can arise. This might include discovering rotted framing around windows, requiring extensive repairs before new windows can be installed. Similarly, problems with underlying sheathing or water damage might be revealed during siding removal, necessitating additional work and materials. These unexpected repairs can significantly impact the project’s overall cost, emphasizing the importance of contingency planning. For instance, discovering extensive termite damage during siding removal could add thousands of dollars to the project’s final cost.
Contingency Budgeting
Incorporating a contingency budget is a crucial step in managing the financial aspects of a window and siding replacement. This involves setting aside a percentage of your total project budget to cover unexpected expenses. A reasonable contingency ranges from 10% to 20%, depending on the complexity of the project and the age of your home. For example, on a $20,000 project, a 15% contingency would mean setting aside an additional $3,000. This buffer helps absorb unforeseen costs, preventing project delays or compromising on quality due to budget constraints.
Potential Unexpected Costs, Average cost for windows and siding
It’s wise to anticipate potential unforeseen costs. These could include:
- Unexpected structural issues were discovered during demolition.
- Additional labor costs due to unforeseen complexities.
- Higher-than-anticipated material costs due to market fluctuations.
- Damage to surrounding property during installation.
- Increased permit fees due to unforeseen project changes.
- Costs associated with correcting mistakes during installation.
- Unforeseen delays lead to increased labor costs.
Final Conclusion

Source: woodbridgehomesolutions.com
Replacing windows and siding is a significant investment, but with careful planning and understanding of the cost factors involved, you can transform your home’s curb appeal and energy efficiency. Remember to factor in all potential costs – materials, labor, permits, and potential unforeseen issues – to ensure a smooth and financially sound renovation. By considering the various options and their associated costs, you can confidently choose the best solution for your home and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average lifespan of different siding materials?
Vinyl siding typically lasts 20-30 years, wood siding 20-50 years (depending on maintenance), fiber cement siding 30-50 years, and metal siding 40-plus years.
Do I need permits for window and siding replacement?
Permits are often required, depending on local regulations. Check with your local building department for specific requirements.
Can I finance window and siding replacement?
Yes, many financing options are available, including home improvement loans and credit cards. Shop around for the best rates.
How much should I budget for unexpected costs?
It’s wise to include a 10-20% contingency in your budget to cover unforeseen issues like rotted wood or unexpected repairs.
What is the best time of year to replace windows and siding?
Spring and fall generally offer the best weather conditions for installation, avoiding extreme heat or cold.
Comments are closed.